API Content
Rendering content from an API remains one of the most popular use cases of the Vyuh Framework. This is expected as most real-world apps fetch data from an API and render it as per the brand guidelines.
In this guide, we will see how to integrate a third-party API and render it as per our needs.
1. Identifying a Third-Party API
For this example we will use the DummyJSON API, which provides a variety of endpoints for products, carts, recipes, todos, and more.
We will use two endpoints for products:
- Products list (
https://dummyjson.com/products): shows a list of products with query parameters to control thelimitandskip. - Products search (
https://dummyjson.com/products/search?q=<text>): allows searching for products with search terms. It also supports thelimitandskipquery parameters.
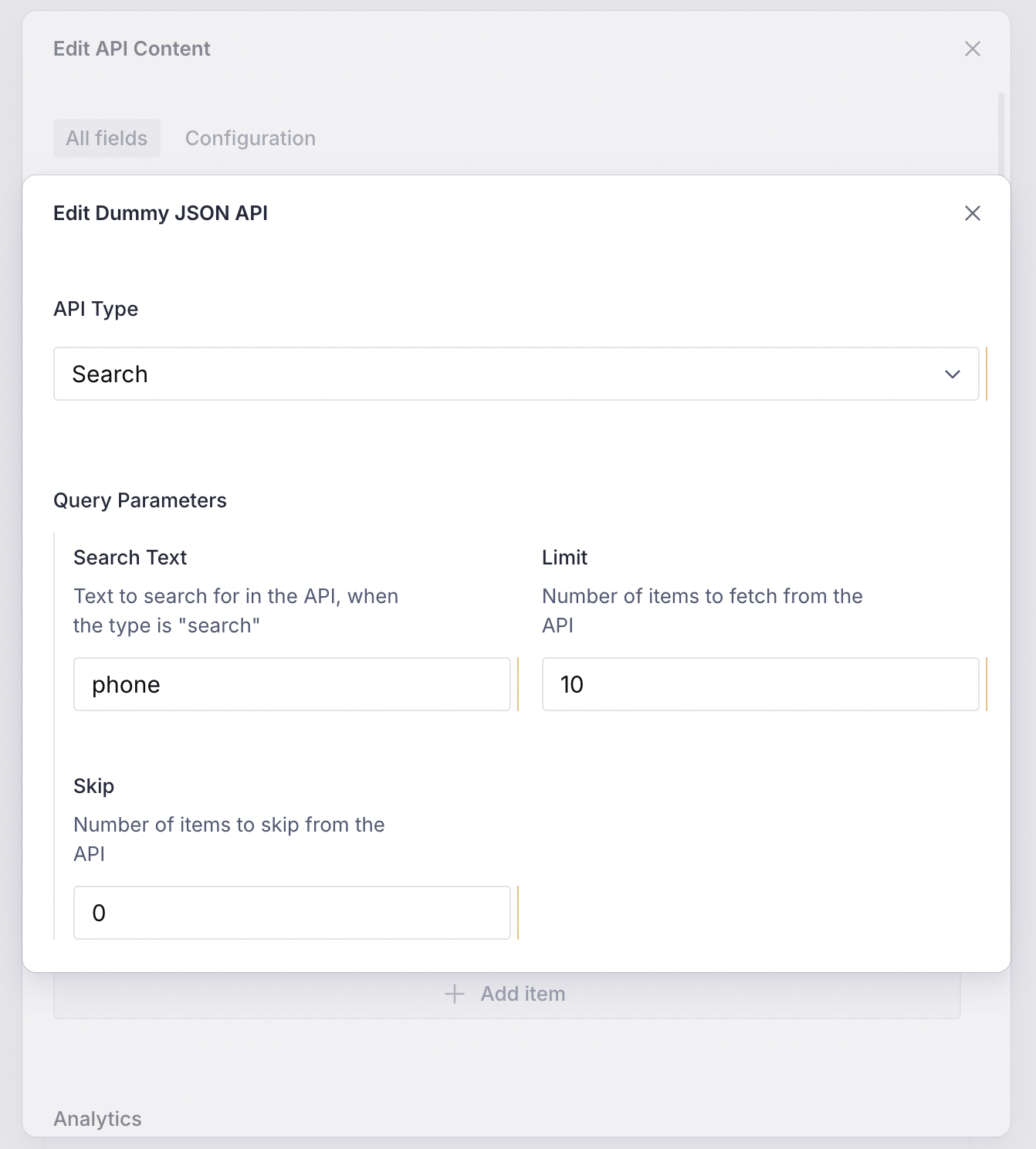
2. API Configuration Schema for the CMS
Based on the parameters above, here is a schema that can be configured from the CMS. It allows changing the limit, skip, and searchText parameters:
import { defineField, defineType } from 'sanity'
export const dummyJsonApi = defineType({
name: 'misc.apiContent.dummyJson',
type: 'object',
title: 'Dummy JSON API',
fieldsets: [
{
title: 'Query Parameters',
name: 'queryParameters',
options: { columns: 2 },
},
],
fields: [
defineField({
name: 'type',
title: 'API Type',
type: 'string',
validation: (Rule) => Rule.required(),
initialValue: 'products',
options: {
list: [
{ title: 'Products', value: 'products' },
{ title: 'Search', value: 'search' },
],
},
}),
defineField({
name: 'searchText',
title: 'Search Text',
type: 'string',
fieldset: 'queryParameters',
}),
defineField({
name: 'limit',
title: 'Limit',
type: 'number',
validation: (Rule) => Rule.min(1).max(50),
initialValue: 10,
fieldset: 'queryParameters',
}),
defineField({
name: 'skip',
title: 'Skip',
type: 'number',
validation: (Rule) => Rule.min(0),
initialValue: 0,
fieldset: 'queryParameters',
}),
],
})Export it in the FeatureDescriptor:
import { FeatureDescriptor } from '@vyuh/sanity-schema-core'
import { APIContentDescriptor } from '@vyuh/sanity-schema-system'
import { dummyJsonApi } from './content/dummy-json-api.ts'
export const misc = new FeatureDescriptor({
name: 'misc',
title: 'Miscellaneous',
contents: [
new APIContentDescriptor({
configurations: [dummyJsonApi],
}),
],
})Now our API configuration shows up on the CMS and we can configure it as needed.
3. API Configuration on the Flutter Side
On the Flutter side, extend the ApiConfiguration<T> abstract class. You need to override two methods:
invoke(BuildContext context): Invokes the API and fetches the content.build(BuildContext context, T? data): Renders the data as per the design system.
@JsonSerializable()
final class DummyJsonApiConfiguration
extends ApiConfiguration<ProductList> {
static const schemaName = 'misc.apiContent.dummyJson';
static final typeDescriptor = TypeDescriptor(
schemaType: schemaName,
fromJson: DummyJsonApiConfiguration.fromJson,
title: 'DummyJSON API',
);
final DummyJsonProductApiType type;
final String? searchText;
final int limit;
final int skip;
DummyJsonApiConfiguration({
required this.type,
this.searchText,
required this.limit,
required this.skip,
}) : super(schemaType: schemaName, title: 'DummyJSON API');
factory DummyJsonApiConfiguration.fromJson(Map<String, dynamic> json) =>
_$DummyJsonApiConfigurationFromJson(json);
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context, ProductList? data) {
if (data == null) {
return empty;
}
return ListView.builder(
itemBuilder: (_, index) {
final item = data.products[index];
return ProductTile(item: item);
},
itemCount: data.products.length,
);
}
@override
Future<ProductList> invoke(BuildContext context) async {
final parameters = {
if (type == DummyJsonProductApiType.search)
'q': searchText,
'limit': limit,
'skip': skip,
}.entries.map((x) => '${x.key}=${x.value}').join('&');
final basePath = switch (type) {
DummyJsonProductApiType.products =>
'https://dummyjson.com/products',
DummyJsonProductApiType.search =>
'https://dummyjson.com/products/search',
};
final response =
await vyuh.network.get(Uri.parse('$basePath?$parameters'));
final list =
ProductList.fromJson(jsonDecode(response.body));
return list;
}
}Notice the use of vyuh.network for invoking the API. This is the recommended way of invoking APIs in Vyuh.
Include it in the Flutter FeatureDescriptor:
final feature = FeatureDescriptor(
name: 'misc',
title: 'Misc',
extensions: [
ContentExtensionDescriptor(
contents: [
APIContentDescriptor(configurations: [
DummyJsonApiConfiguration.typeDescriptor,
]),
],
),
],
);4. API Content in Action
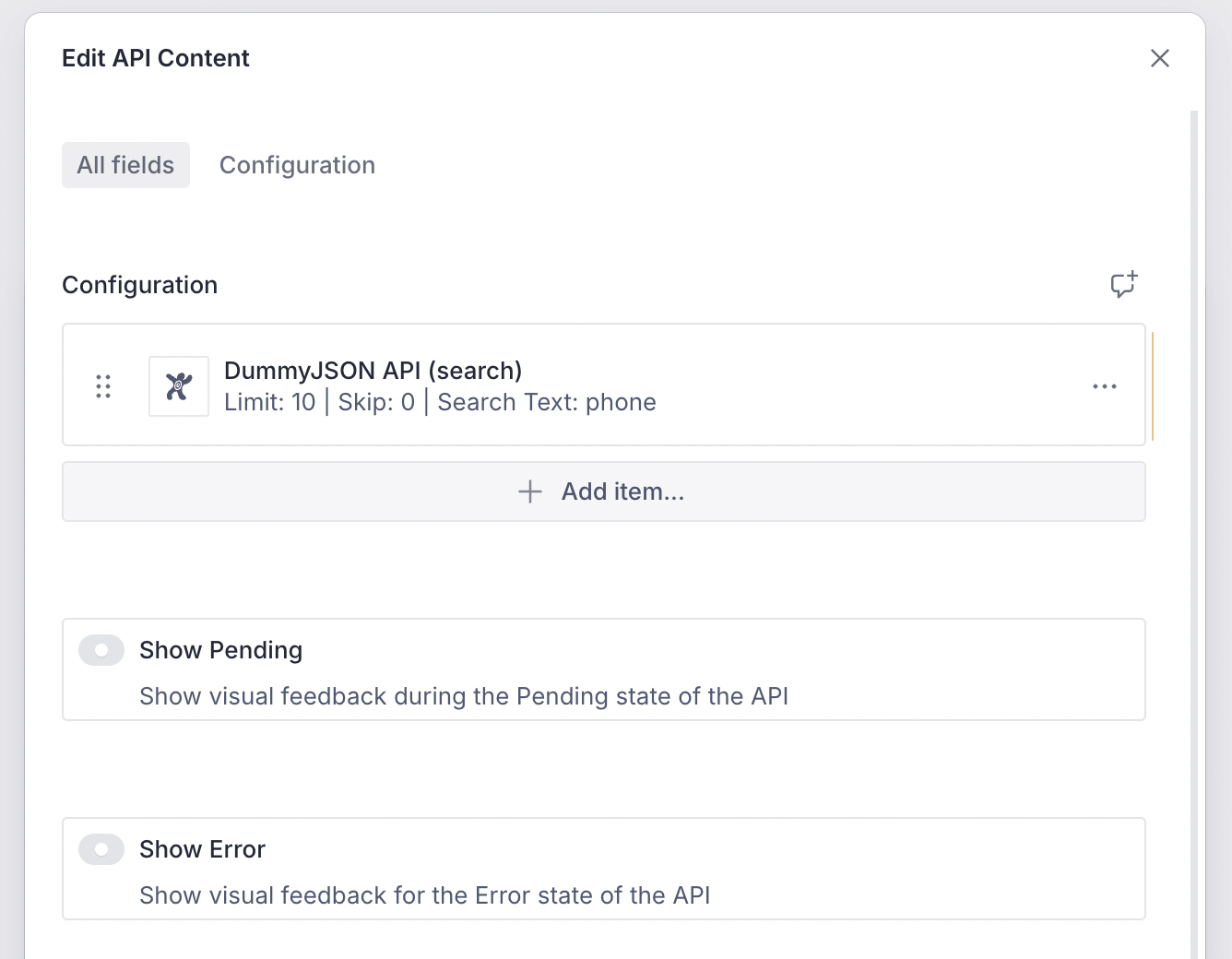
You can now include the API Content block on the CMS and configure it with the DummyJSON API.
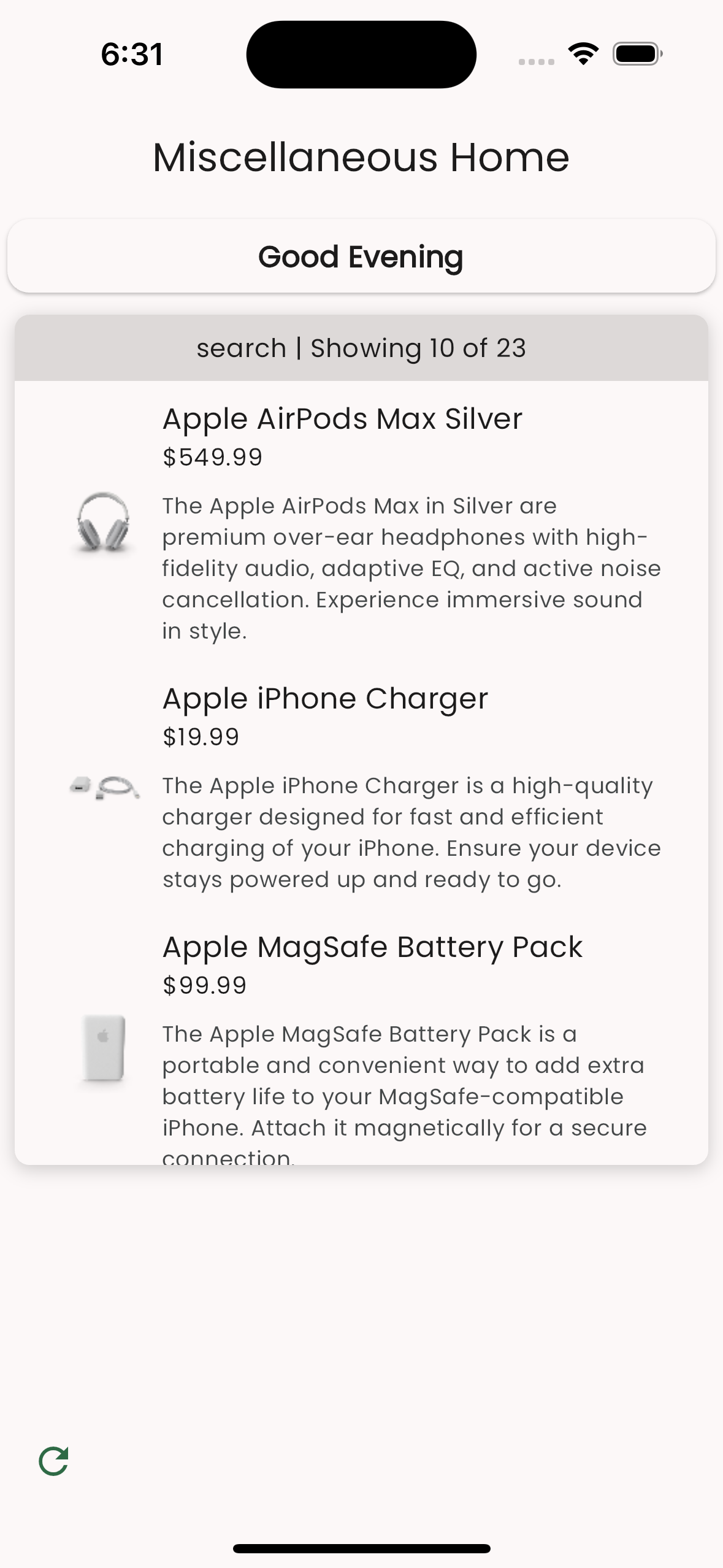
On the Flutter side, after loading the page which has this content block, you will see the products rendered with custom styling.
Summary
Vyuh has rich provision to integrate custom API endpoints and render their responses. To configure it on the CMS, define a custom schema with the APIContentDescriptor.
There is a similar task on the Flutter side, where you take care of the implementation details of invoking the API and rendering it. Together you have a powerful, configurable API Content block that can be changed dynamically from the CMS.